Forex basics
Forex basics are the necessary knowledge and terms, without which you can’t start a trading career. Here you will learn what spread, options, types of accounts, pending orders and scalping strategies are. You’ll find answers to questions about how to choose a broker and trade on news with minimal risk, learn how to choose currency pairs. This section will reveal the secrets of training features and help you understand how to earn on Forex and succeed, while reducing risks and losses.
- Details
- Written by Jeremy Stanley
- Category: Forex basics
- Hits: 3880
Many people do not understand Forex principles correctly: they think that you need to buy, sell and that’s it. But that is not true. Here we will look at the foundations of this market work, but first let’s try to understand what Forex is and what it is not.
Forex is an international currency market and it stands for “currency exchange” or Foreign Exchange – the first two syllables are taken. The official date of Forex foundation is 1971 and the object for trading is currency form different countries. The principles of Forex work are governed by these factors – the condition of the economy of the countries whose currency take part in these trades.
Curiously enough the deals are made with high speed in the wide diapason of crediting. That allows getting the possibility to receive significant margin or profit from the operation, in case of some investment. Forex is similar to roulette with red or black, with the only difference: here currencies stand for black or red.
It is important to study more closely the Forex principles, because after understanding the essence of their functioning it will be possible to see the real situation when you face it, after starting to trade on this unique exchange which opens new opportunities for anyone.
- Details
- Written by Jeremy Stanley
- Category: Forex basics
- Hits: 3759
Fundamental analysis of Forex market is one of the main factors, according to which an experienced trader can build his own trading strategy. But it is worth noting that by using this analysis, any trader has to possess the information on how to better use the data. First of all one has to take into account that it is advisable to utilize any information, provided by fundamental analysis of Forex market, only jointly with technical analysis, and with other indicators. Only in this case you can be sure that your strategy is successful and will bring significant profits, since comprehensive approach allows correcting possible mistakes and eliminating possibility of errors at most.
Fundamental analysis of Forex market is directed at determination of dependence of national currency of certain country from external factors. Such data help traders that prefer working with the news, i.e. make deals right after reading an important economic or political information that influences the currency value. It is pretty easy to use fundamental Forex market analysis, because important news as a rule appear seldom and regular reports come out once a month or even less.
- Details
- Written by Jeremy Stanley
- Category: Forex basics
- Hits: 4361
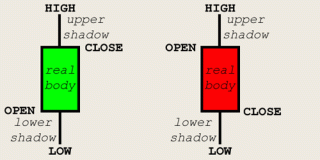
Traditionally three main methods of creating rates graphs are singled out: linear, with bars or candlestick charts. Of course there are some other methods of creating rates graphs, such as noughts and crosses and other unpopular methods.
Lately candlestick chart has gained great popularity. They have appeared in the Western world recently – in 80-s, in contrast with linear and, standard for American markets, bar graphs. However in Japan, where they originated from, these charts have been in use even before the creation of share markets, when analyzing trading of primary products.
The candlestick graphic analysis was “founded” by Steve Nisson who wrote the book “Candlesticks. Graphic analysis of markets”, where he described means of building candlesticks and methods of analyzing the market, as well as the main graphic patterns of candlestick charts.
The candlestick chart is a sum of candlesticks that like the bars are built on the basis of specified time slot (a minute, an hour, 4 hours, a day, a week, a month or any other).
Japanese candlesticks have the following characteristics: